What is Obesity?
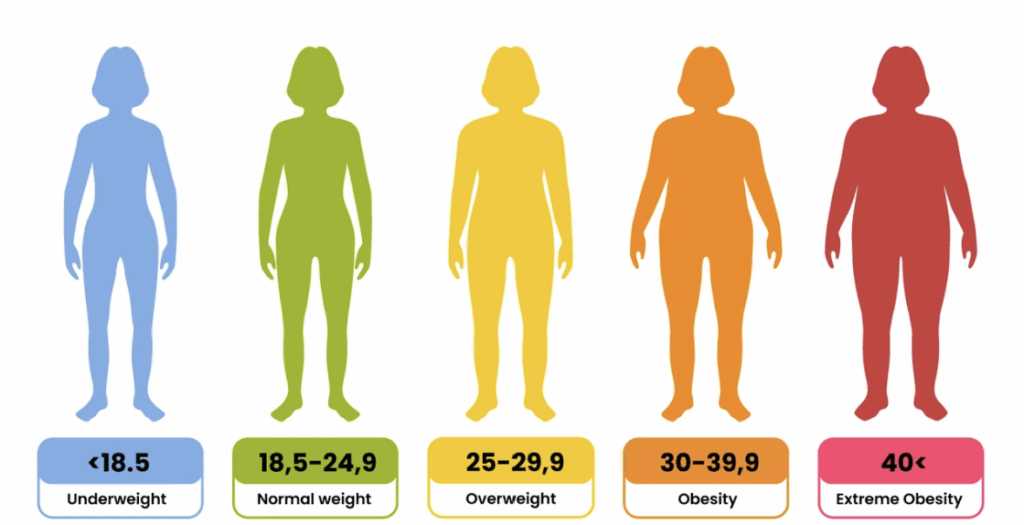
Many people put obesity down as a number. When we look at it this way, we are talking about BMI. A calculation based on our height and weight. In these terms:
- Obesity is over 30 BMI
- Overweight is between 25 and 29.9 BMI
But what does this look like?
Obesity is an accumulation of excessive fat and is associated with health risks. another measure of risk is waist circumference. A larger waist circumference is an indicator for fat around the organs which is dangerous to our health. A waist circumference above 80 cm for women and 94 cm for men is the starting point for concern.

Risks from being overweight or obese
There are many risks from having excess fat. Being overweight or obese can create a burden on the body as the body is required to support more weight than is healthy. Inflammation, pain and discomfort are part of the excess weight burden, but the body must also manage hormonal imbalances, and additional demands on the cardiovascular system. Combined with the lifestyle factors that may have led to excess weight (diet, and inactivity), the body is also needing to potentially manage digestive issues, sleep issues, mental health issues, diabetes, and cholesterol. The body can become quite unwell, and unfortunately, many of the conditions that are caused by excess weight can also make it more challenging to lose weight.
Below is a list of health risks associated with obesity and being overweight. These include:
- insulin resistance
- high blood pressure
- atherosclerosis
- cardiovascular disease
- stroke
- some cancers including breast
- endometrial and colon cancer
- type 2 diabetes (non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus)
- gall bladder disease
- polycystic ovarian syndrome
- musculoskeletal problems such as osteoarthritis and back pain
- gout
- cataracts
- stress incontinence
- sleep apnoea
Due to the increased risk of disease, death can result.

What causes obesity?
There are many contributing factors that can lead to a person becoming overweight or obese.
Lifestyle
Our lifestyle plays a huge role in weight management. How active our job is, what activities we participate in eg sports, walking, impact how much energy we use daily. An active person compared to an inactive person can eat more because they have a higher energy requirement.
genetics
Obesity can run in families. This can be because of inherited lifestyle factors eg. growing up in an active household or inactive household, or a family that eats more healthily or unhealthily. But, there is also a genetic component. Your genes can affect the amount of fat you store, your metabolism and appetite. These factors can be mediated with changes to lifestyle and diet.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9569701/
diet
What we eat and how much we eat is a major factor in weight loss and gain. While the amount of calories matters, so does the nutritional value of the foods we eat. If we eat too much of any food we can also gain weight even if it is ‘healthy’.
social environments
We behave differently around food in different social environments. For example people tend to eat more if they eat while watching tv. They also may snack more, eat more or drink more alcohol if they are out with friends. We also may have either active or sedentary social environments. Some people may be supportive or unsupportive to our goals also. Understanding our social habits helps us to manage our impulses.
economic costs
Being overweight or obese can come as a result of financial choices. When we look at the dollar value of food, sometimes it is cheaper to buy non-nutritious food that is high in calories. eg. unhealthy takeaway is often much cheaper than healthy takeaway. We may also find it difficult to afford gym memberships or sporting activities. Though we often don’t factor in the costs of being inactive to our health.
medical conditions
Some medical conditions make it more difficult to maintain our weight. This can be from the condition itself or from medication for the condition. Medical conditions that affect weight management include Cushing’s syndrome and PCOS. Medications that impact weight management include corticosteroids, antidepressants, and seizure medications.
age
As we age it can become harder to manage our weight. One of the main reasons is loss of muscle which results in a slower metabolism. Menopause plays a role in women and fat distribution can also change at this time.
other
Factors such as getting enough quality of sleep, quitting smoking, drinking alcohol and pregnancy can also lead to difficulties in weight management.
Consequences of obesity
Mortality
Obesity is associated with an increased risk of premature death. Obese individuals have a 50-100% increased risk of premature death for all causes compared to healthy weighted people. Life expectancy can be 9 years less.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK44210
illness
Obesity is also associated with increased risk of illness. This includes many cancers, cardiovascular diseases, but also common illnesses such as colds and flus due to immune system impairment. A non-exhaustive listed of illnesses is highlighted at the top of the page.
mental health
Obesity can impact people’s mental health. People with Obesity may have poor body image, can suffer from bullying, anxiety, and self-esteem issues. Obese children and adults are also more likely to suffer from depression.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3749079/
socio-economic
Obesity is costly. Consider individual financial costs of healthcare and time off work due to obesity related illness. The financial costs to society are also great in the same areas. A 2021 report by the Obesity Collective stated a direct econmonic cost of $8.6 billion AUD, and indirect of $14.5 billion. This include the costs of healthcare, lost productivity, and welfare costs associated with premature mortality and reduced quality of life. As a healthcare cost, excess weight accounts for similar costs as smoking.
How life events play a part
Life events, especially those which cause stress or trauma, can make it more difficult for some people to manage their weight. This includes life-changing events such as divorce, serious injury, and life-threatening events. Homelessness, unemployment, or anything that causes negative stress in a person can be a factor in their ability to manage their weight.
Other life events can impact our management of weight, but are not specifically negative. For example, birthdays, weddings or anniversaries where we have habits of indulgence. Specific stages of our life such as menopause, adolescence, ageing, or pregnancy may affect our metabolism and weight management.
Barriers to weight loss
There are many barriers to weight loss. If we understand which are relevant to us, then we can tackle these and manage them to have success in our weight management plan. These same barriers are likely to be related to why you have gained excess weight in the first place.
Barriers include:
Time – with long work hours or other commitments, some people may find it more difficult to find time to exercise, cook or plan meals.
Support – Support, whether from family, friends or coworkers, is an important factor in weight management. Doing it alone is a tough route and success is improved with the right kind of support. It can be especially hard when some people do not support your health goals.
Self-esteem/confidence – how we feel about ourselves is a crucial component to success. For a program to be successful, we need to have the belief that it can be. Factors such as body image can hold us back. Embarrassment avoidance may also be a factor in not taking action.
Knowledge regarding exercise – Education about exercise is an area that some people may be lacking. Having a basic understanding of how to start can support a person to get started.
Energy – Obesity can be exhausting, and fatigue is a common symptom of being overweight or obese. Therefore, it can be difficult for some people to become motivated when they are already tired. Even though an improved diet and exercise can improve energy levels, this can be hard to overcome.
Convenience – Modern life has it’s conveniences which don’t support maintaining a healthy weight. Many conveniences, such as technology and transport, mean we are less active perhaps than we need to be, because it is far more convenient to drive to the shops than to walk 30 minutes there and back. Takeaway food is also far more convenient than home-cooked meals, but for the most part, it is far more unhealthy for us.
Enjoyment – We want what we enjoy and avoid what we don’t. This can stem from a childhood where we hated our vegetables or disliked sports. Some people develop an idea about healthier options as being less enjoyable. But healthy options can be enjoyable; it just may take some time and effort to discover this, including retraining our view of what is enjoyable.
Being injured, having an illness, or disability – It can be challenging for those with illness, injury or other disability to be manage their weight. This can be from physical impairment that makes it difficult to exercise or exercise regularly, finding a diet suitable for their illness, or due to psychological barriers from their condition.
